Posterior Tibial Tendonitis
- Best Asics Shoes for Flat Feet - October 25, 2024
- Best Running Shoes for Flat Feet - October 22, 2024
- Posterior Tibial Tendonitis - October 21, 2024
Understanding the Posterior Tibial Tendon and Its Role in Foot Stability
The Posterior Tibial Tendon is a key structure that helps support your foot’s arch and maintain stability while walking or running. It runs along the inner side of the ankle, connecting the Posterior Tibialis muscle in your lower leg to the navicular bone in your foot.
This tendon is essential for movements like foot inversion (turning the foot inward) and plantarflexion (pointing the toes downward). However, when it becomes overworked or strained, Posterior Tibial Tendonitis (Tendinopathy) can develop, leading to pain, inflammation, and potential arch collapse if left untreated.
What Causes Posterior Tibial Tendonitis?
Several factors can contribute to Posterior Tibial Tendon pain, including:
1. Sudden Increase in Activity
- Walking significantly more steps than usual
- Increasing running distance, speed, or intensity too quickly
- Training for high-impact sports like marathons or sprinting
2. Ankle Injuries and Foot Structure Issues
- A history of ankle sprains or fractures can alter foot mechanics, putting excess strain on the tendon
- Flat feet or collapsed arches overstretch the tendon, leading to inflammation
- Stiff big toe or high arches can also cause compensation, resulting in tendon overload
3. Footwear Choices
- Wearing unsupportive shoes—such as sandals or flat, flexible shoes—can increase stress on the tendon
- Even supportive sandals like Birkenstocks may not provide enough arch support compared to motion-control running shoes
4. Excess Body Weight
- Carrying extra weight increases pressure on the tendon, making it more prone to irritation.
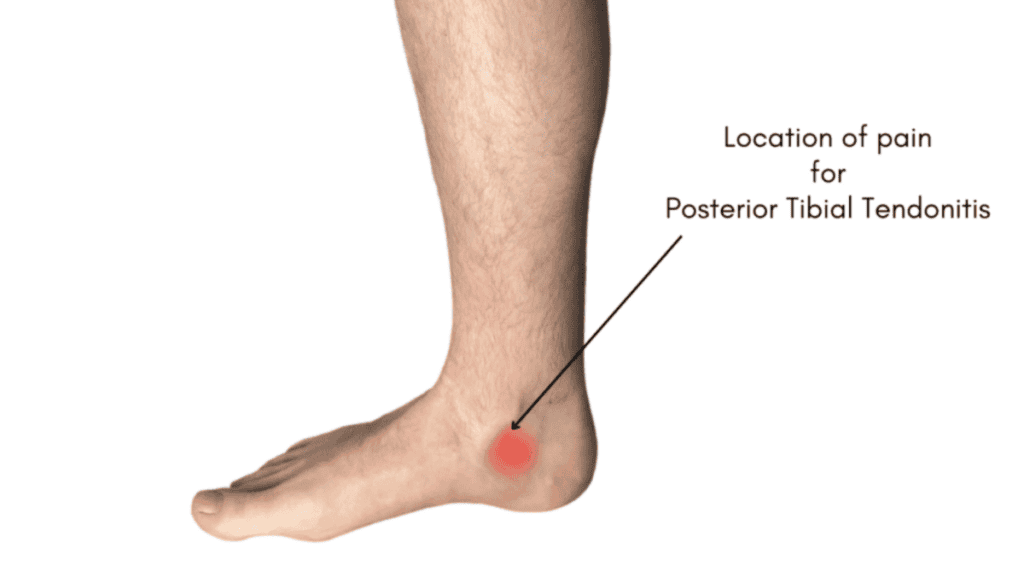
Recognising the Symptoms of Posterior Tibial Tendonitis
Early-Stage Symptoms:
✔ Pain along the inner ankle, especially when walking or running
✔ Swelling in the affected area (though bruising is uncommon)
✔ Morning stiffness and discomfort, which improves after moving for about an hour
Progression of Symptoms:
✔ Pain extends into the arch of the foot
✔ Clicking or crunching sensations in the ankle
✔ Difficulty walking or standing for long periods
✔ The arch may gradually flatten, leading to Adult-Acquired Flatfoot
How Is Posterior Tibial Tendonitis Diagnosed?
A Physical Therapist or healthcare provider can diagnose Posterior Tibial Tendonitis through:
✔ Manual testing – Pressing along the tendon to check for pain and swelling
✔ Resistance testing – Moving the foot inward or downward to assess tendon function
✔ Heel raise test – Difficulty or inability to perform single-leg heel raises may indicate dysfunction
Imaging Tests for Severe Cases:
🔹 Ultrasound – Identifies tendon inflammation or small tears
🔹 MRI – Provides a detailed image of tendon structure
🔹 X-ray – Rules out bone-related issues, such as arthritis
Managing Posterior Tibial Tendonitis at Home
For mild cases, follow these at-home treatment strategies:
✔ Rest – Reduce high-impact activities like running or jumping
✔ Ice Therapy – Apply ice packs for 10-15 minutes to decrease inflammation
✔ Supportive Footwear – Wear motion-control running shoes or cushioned insoles
✔ Ankle Braces or Taping – Provides extra stability and offloads the tendon
Professional Treatment Options for Posterior Tibial Tendon Pain
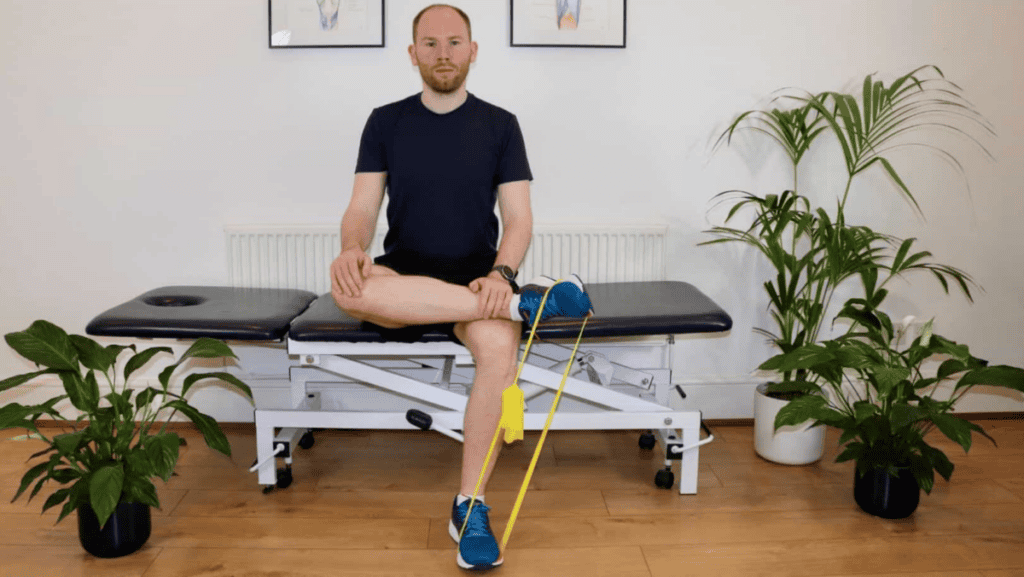
1. Physical Therapy
✔ Strengthening exercises – Focus on the Posterior Tibialis muscle, Soleus, and foot intrinsics
✔ Taping techniques – Offloads the tendon to reduce strain
✔ Gait analysis – Identifies biomechanical imbalances contributing to tendon overload
2. Custom Orthotics & Braces
✔ Insoles or orthotics – Provide arch support and correct foot mechanics
✔ Ankle braces – Offer short-term relief for acute pain
3. Activity Modification
✔ Switching to low-impact exercises (e.g., swimming or cycling) can aid recovery
✔ Runners may need to adjust their training plans to avoid re-injury
4. Medical Interventions
✔ Steroid injections – May provide temporary relief, but long-term use weakens the tendon
✔ Surgery – Reserved for severe cases, particularly when arch collapse occurs
How Long Does It Take to Recover from Posterior Tibial Tendonitis?
Recovery Timeline:
🔹 Mild cases: 6 weeks with proper treatment
🔹 Chronic cases: 12+ weeks, especially if there is tendon degeneration or arch collapse
💡 Following a structured rehab plan with a Physical Therapist is crucial for long-term recovery and injury prevention.
Final Thoughts
Posterior Tibial Tendonitis is a common but manageable condition affecting the inner ankle and arch. Early intervention with proper footwear, strengthening exercises, and physical therapy can prevent progression and long-term foot issues.
If symptoms persist, consider seeking professional help to explore custom orthotics, gait analysis, or advanced treatment options.
Expert Advice from Flawless Physio
Written by James McCormack, a lower limb specialist with extensive experience in treating foot conditions. If you’re dealing with any of the issues mentioned in this article, seeking advice from a qualified healthcare professional is important. James is available for both virtual consultations and face-to-face appointments in his London clinic.
