Midfoot Spain
- Best Asics Shoes for Flat Feet - October 25, 2024
- Best Running Shoes for Flat Feet - October 22, 2024
- Posterior Tibial Tendonitis - October 21, 2024
What is a Midfoot Sprain?
Ligaments attach bones to bones to provide stability, and alongside the positional layout of the bones in the midfoot, they provide structural integrity to the midfoot.
However, if these ligaments become overstretched through repetitive movement or a sudden twist, it results in a midfoot sprain. The midfoot is the part of the foot connecting the heel bones to the forefoot, and it consists of 5 bones: the cuboid, navicular, medial, intermediate and lateral cuneiform bones.
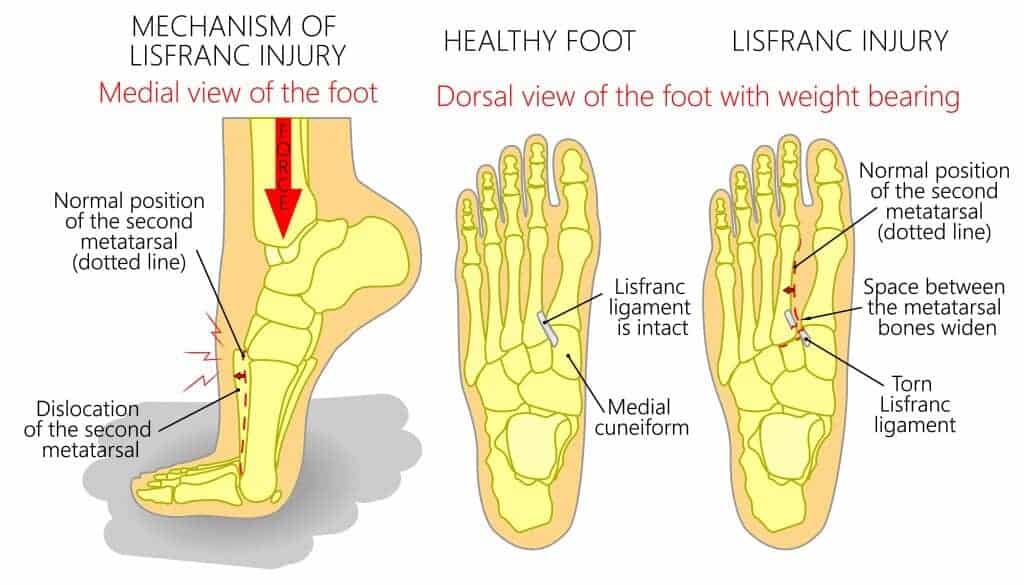
The most common and well-known midfoot sprain is a Lisfranc Injury. This is the keystone to the foot, and a severe sprain requires immediate assessment. We will cover that and more in this article.
Symptoms
Depending on the severity of the sprain, symptoms can alter from mild pain when weight bearing and walking to being unable to weight bear due to high pain levels. If there is an injury of the 2nd metatarsal, this can result in a Lisfranc injury that causes bruising under the foot, swelling and, in some cases, a loss of foot arch height.
Patients often find it difficult or cannot do a single leg heel raise while they mind activities such as hopping or running unbearable.
Swelling is often immediate in onset and may continue to increase over 48 hours, resulting in a throbbing sensation at rest. As a result, the patient may experience night pain and stiffness when walking in the morning.
Causes
The most common cause of a midfoot sprain is windsurfing or horse riding, as the foot is held in position by a stirrup, and a sudden twist rotates the midfoot, causing a midfoot sprain.
We also see this in sports such as football and basketball when an athlete trips or falls while another athlete is standing on their foot. Other causes include falls for 3 metres or more and car crashes, making up 31% of cases. It is common for them to occur along sprains of the lateral ankle.

Diagnosis
If you have any symptoms of a Lisfranc injury, seeing an experienced medical professional is essential.
X-ray is the first port of call to establish a diagnosis, typically Standing, lateral, AP, and 30º Oblique scans. Clinicians should also examine for a ‘fleck sign’ on imaging.
Sometimes, a CT Scan is required, while an MRI may be performed to confirm the stasis of the surrounding soft tissues.
Treatment
Regardless of the severity of a midfoot sprain, therapists often consult with orthopaedic consultants on the best treatment for each case.
Physiotherapy
If the fracture is stable, then in most cases, 6-8 weeks in a walker boot is recommended. This is followed by 2 weeks of weaning out of the boot into a stable trainer.
Physiotherapy commences after the initial 6 weeks in a boot. A patient may be provided with a brace or taping for additional support. Non-weight-bearing band exercises are safe in the early stages of rehabilitation.
A specific weight-strengthening and stability rehabilitation program is created for the patients following a physical assessment and gait analysis. Most mild cases of a midfoot sprain make a complete recovery.
Surgery of severe cases often involves a screw to stabilise the midfoot, and recovery from this procedure takes up to 6 months.
Some cases may require added stability from a custom insole, while shoe advice is helpful.
_______________________________________________________________________
We are specialists in treating foot conditions such as midfoot sprains, and you can see one of our Foot and Ankle Specialists in our clinic in Fulham, South West London.
Related Articles
Best Exercises for Flat Feet – Bone Spur on Top of the Foot – Foot Pain Chart
Feel Good, Move Well, Be Better
