Shin Splints vs Stress Fracture
- Best Asics Shoes for Flat Feet - October 25, 2024
- Best Running Shoes for Flat Feet - October 22, 2024
- Posterior Tibial Tendonitis - October 21, 2024
Key Differences
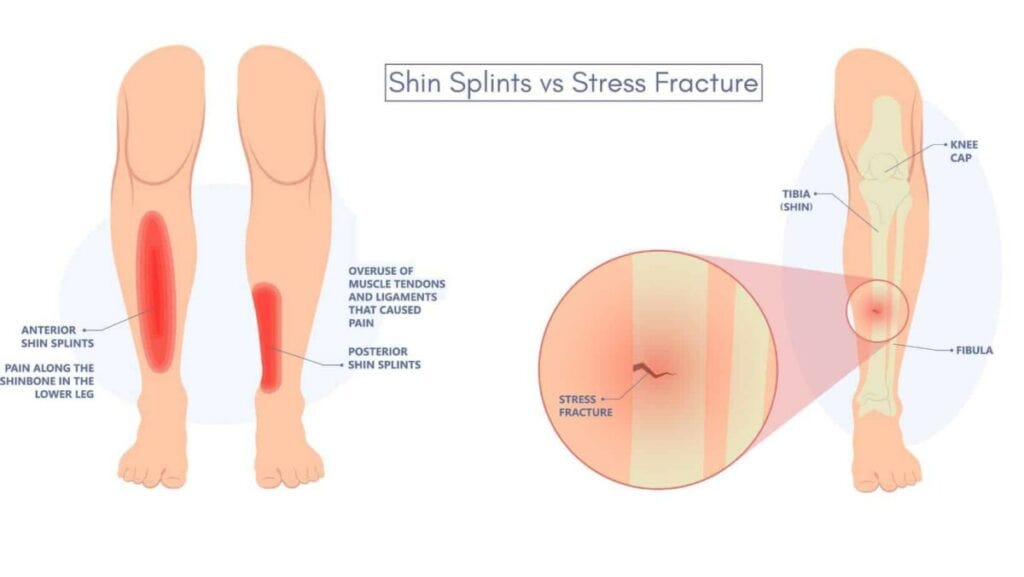
It can be difficult to clinically identify the key differences between Shin Splints (Medial Tibial Stress Syndrome) and a Tibial Stress Fracture, as the location of pain is almost identical.
The primary difference between shin splints and stress fractures is that shin splints affect the outer layer of the shin bone, causing irritation and inflammation of the outer connective tissue called the periosteum. In contrast, a Stress Fracture causes a small hairline-sized break in the bone.
There are key factors in relation to symptoms and clinical presentation that provide a clear framework to decipher between these two diagnoses, which we will cover in this article.
Symptoms
Shin splints cause pain greater than 10cm on the front or inside of the shin bone, whereas stress fracture symptoms are usually at a specific point or less than 10cm on the shin bone.
Shin Splints are often painful at the beginning of exercise and can improve when you warm up before worsening. At the same time, a stress fracture is often immediately painful on weight bearing and worsens with impact exercise.
Both conditions can cause sharp pain on impact, especially with activities such as hopping and running.
Causes
The primary causes of Shin Splints and Stress Fractures are very similar. Previous beliefs included irritation and bone bending from the impact of landing. However, our current understanding is that both injuries result from tibial rotation and stress from the attaching plantar flexors; Soleus, and Posterior Tibial muscles.
As a result, activities that involve high plantar flexor force, such as hopping, jumping and running, are a primary cause, especially if there is a sudden increase in these activities.
Bone health conditions such as Osteopenia and Osteoporosis can increase your likelihood of developing a Stress Fracture.
Less common causes are changes in footwear.

Diagnosis
A Physical Therapist can diagnose both conditions based on a patient’s symptoms and a Physical Assessment.
A cluster of tests should be performed to help with the diagnosis. Pain on single leg hopping and palpation of the posteromedial tibial of less than 10cm provided a sensitivity score of 100%.
Pain greater than 10cm should heighten your suspicion of shin splints rather than a stress fracture.
In contrast, a Physical Therapist can clinically suspect a Stress Fracture, but a scan is required to confirm the diagnosis. An X-ray can identify a Stress Fracture. If the scan returns as normal but there is a high clinical suspicion of a stress fracture, then it is recommended that a patient is sent for an MRI.
The rationale for this process is that a tibial stress fracture is a high-risk site of injury that can fail to heal without prompt diagnosis and treatment.
Treatment
Stress Fractures
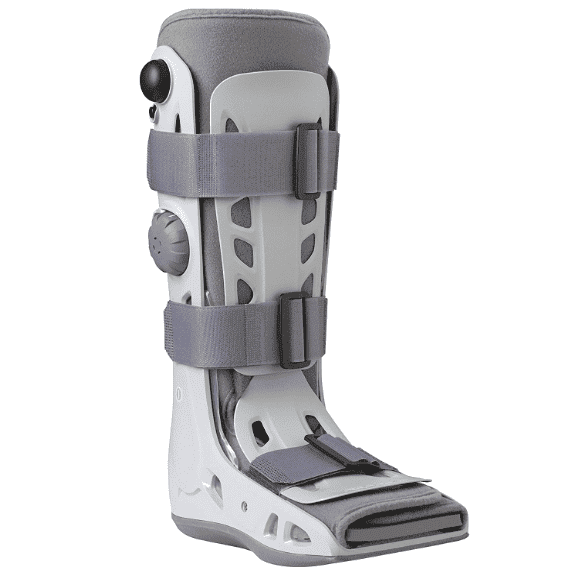
The grade of injury influences treatment for this condition. A low grade may require 1-2 weeks of non-weight-bearing, which can extend up to 8 weeks in a high-grade fracture.
This will progress onto partial weight-bearing while wearing a walker boot and crutches. We normally transition patients into cushioned supportive trainers indoors before progressing to outdoors. Pain levels determine each progression; you should not progress if any pain is present.
A gait and physical assessment of muscular strength and foot and ankle mobility benefit both conditions, while advice on the correct footwear and insoles can help.

Shin Splints
In contrast, you can continue to exercise with Shin Splints. Your Physiotherapist will discuss different impact training options for you as they vary in plantar flexor forces and stress on the bone.
Soleus muscle strengthening should form the primary part of rehabilitation, and this will progress onto plyometric exercises to increase muscle and bone capacity.
Icing and a brace can help reduce Shin Splints pain while cross-training with swimming and cycling, which is beneficial for maintaining cardiovascular health for both conditions.
_______________________________________________________________________
We are specialists in treating foot conditions such as shin splints or stress fractures, and you can see one of our Foot and Ankle Specialists in our clinic in Fulham, South West London.
Related Articles
Insoles for Shin Splints – Bone Spur on Top of the Foot – Foot Pain Chart
Feel Good, Move Well, Be Better
