PTTD: Posterior Tibial Tendon Dysfunction
- Outside Ankle Pain: Running, Standing, Walking - February 14, 2024
- Plantar Fasciitis Taping - January 30, 2024
- Peroneal Tendonitis Taping - January 30, 2024
What is PTTD?
PTTD (Posterior Tibial Tendon Dysfunction) is a condition that affects the Poster Tibial Tendon, leading it to become weak and painful on the medial ankle, resulting in an adult-acquired flat foot.
PTTD Symptoms
PTTD in the early stages can result in pain in the inner ankle that is worse with impact activities such as walking, running or jumping. There is often minimal swelling or bruising, while symptoms are often worse first thing in the morning.
As the condition progresses, there may be a visible reduction in the foot’s medial arch and too many toes sign when looking at the foot from behind. In severe cases, pain can develop on the outer ankle as well as the inner ankle.
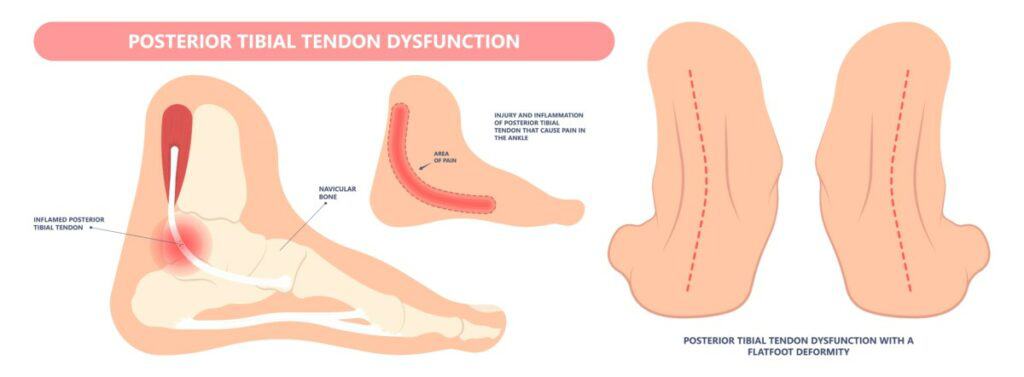
PTTD Causes
PTTD is most prevalent in middle age from the gradual weakening of the Posterior Tibial Tendon. PTTD can also be caused by repetitive ankle sprains, especially medial ankle sprains or a previous ankle fracture.
Obesity plays a significant role in developing PPTD, as excess weight strains the tendon.
PTTD Diagnosis
PTTD can be diagnosed by a clinician such as a Physical Therapist. A Physical examination can identify changes in the position of the foot arch height and too many toes sign. When doing heel raises, a patient may not be able to achieve subtalar joint inversion alongside a minimal capacity of heel raises. We expect most patients to be able to carry out at least 15 single-leg heel raises.
In severe cases of PTTD, an x-ray can help identify arthritis of the ankle joint, but in most cases, an MRI is the preferred form of imaging for PTTD. An MRI can identify swelling and inflammation of the Posterior Tibial Tendon alongside any structural changes to the ankle or the foot.
Treatment for PTTD
In most cases, symptoms can be improved with Physical Therapy. A Physical examination and a gait analysis can identify muscular weakness and imbalances. Strengthening exercises to the Soleus muscles, Posterior Tibial Tendon and intrinsic foot muscles can be highly beneficial for the patient’s symptoms.
Guidance on the correct footwear and the necessity for custom insoles is an essential aspect of treatment for pain relief.
In severe cases, a Posterior Tibial Tendon Brace can reduce pain levels while rehabilitating a patient. A Physical therapist can advise how to manage daily activities such as walking and exercise. We recommend non-impact exercise such as swimming or cycling for patients with PTTD.
Steroid injections are generally avoided for this condition as they can cause the weakening of the tendon and a reduction in a tendon’s capacity for load.
In stage 4 PTTD, surgery may be required due to significant arthritis of the ankle joint.
__________________________________
We are specialists in treating foot conditions such as PTTD and have experts in foot conditions in our clinic in Fulham, South West London.
Related Articles
Posterior Tibial Tendon Dysfunction Orthotics – Overpronation Insoles – Insoles for Flat Feet
